Install OpenStack Juno on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7

OpenStack is a free and open source cloud computing platform developed as a joint project of Rackspace Hosting and NASA. Users primarily deploy it as an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) solution. OpenStack cloud consists of many well know technologies like: Linux KVM, LVM, iSCSI, MariaDB (MySQL), RabbitMQ or Python Django.
OpenStack architecture overview:
- Horizon: web browser user interface (dashboard) based on Python Django for creating and managing instances (virtual machines)
- Keystone: authentication and authorization framework
- Neutron: network connectivity as a service
- Cinder: persistent block storage for instances based on LVM
- Nova: instances management system based on Linux KVM
- Glance: registry for instance images
- Swift: file storage for cloud
- Ceilometer: metering engine for collecting billable data and analysis.
- Heat: orchestration service for template-based instance deployment
In this tutorial we will install OpenStack Juno release from RDO repository on two nodes (controller node & compute node) based on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7.
Environment used:
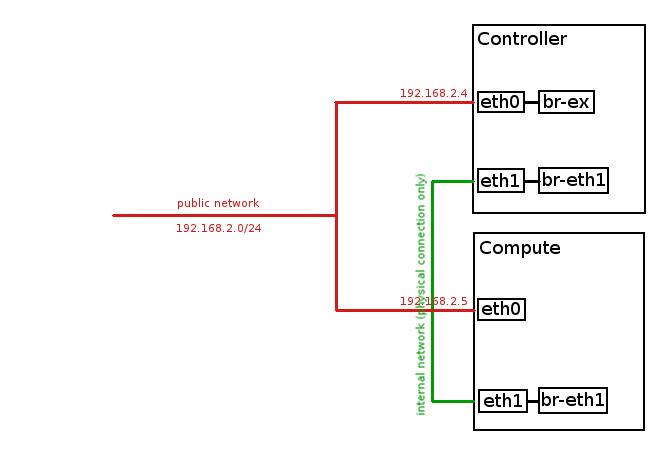
public network (Floating IP network): 192.168.2.0/24
internal network: no IP space, physical connection only (eth1)
public controller IP: 192.168.2.4 (eth0)
public compute IP: 192.168.2.5 (eth0)
Read More